 Recycling preserves resources, minimizes waste sent to landfills and decreases pollution from raw material processing. It plays a crucial role in energy conservation and mitigating climate change by lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, recycling helps preserve natural habitats and biodiversity by reducing the demand for new resource extraction. Efficient recycling practices not only benefit the environment but also foster a sense of responsibility and sustainability.
Recycling preserves resources, minimizes waste sent to landfills and decreases pollution from raw material processing. It plays a crucial role in energy conservation and mitigating climate change by lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, recycling helps preserve natural habitats and biodiversity by reducing the demand for new resource extraction. Efficient recycling practices not only benefit the environment but also foster a sense of responsibility and sustainability.
The mechanical recycling of plastics has been used on an industrial scale for years, but it faces technical and economic limitations. The advancement of chemical and process engineering marks the next crucial steps in enhancing the value chain and promoting material circularity.
Chemical recycling processes break down plastics back into monomers or raw materials, enabling the production of new goods across all plastic applications. The range of chemical recycling processes available is vast, offering immense potential for innovation and sustainability.
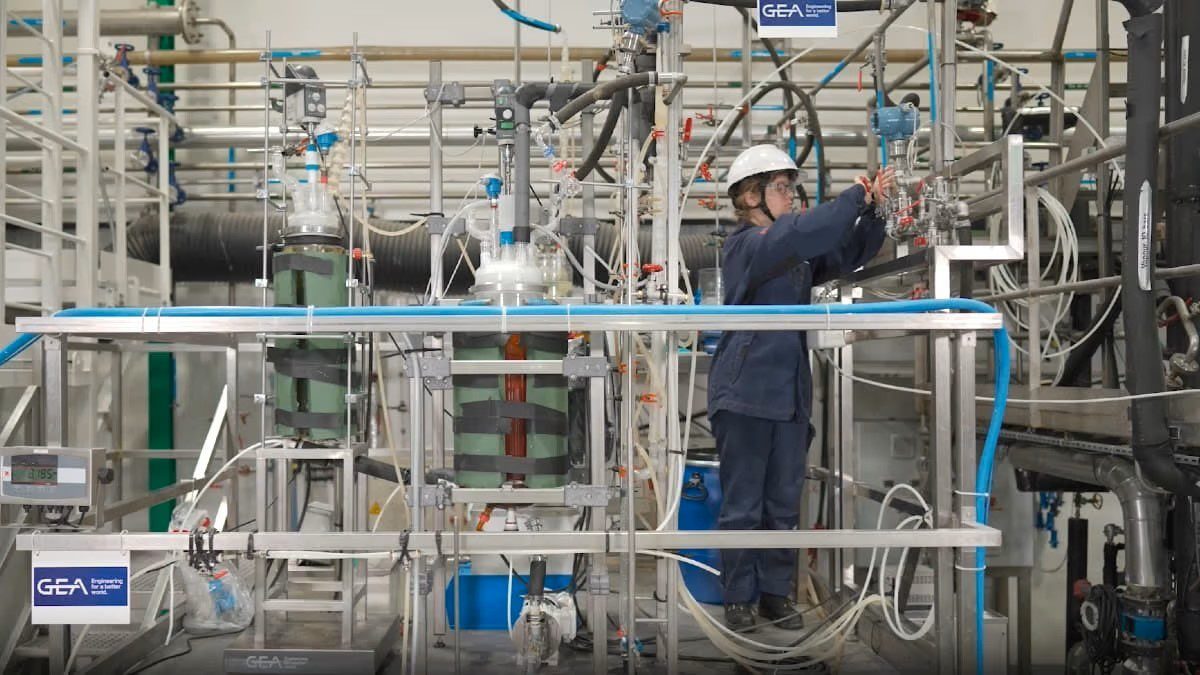

PET crystallization testing at GEA laboratory & test center, Montigny-le-Bretonneux, France.
As leading supplier of process technology and solutions, GEA delivers innovative technologies that enable chemical manufacturers rethink their production processes and waste streams to achieve energy and resource efficiency.
With eco-design expertise and engineering to the most demanding standards, GEA assists manufacturers through and through with a wide range of technologies and tailor-made solutions that address the specific challenges faced by the chemical industry such as:
- Thermal Separation and Crystallization. GEA’s benchmark thermal separation and crystallization technologies enable manufacturers to remove impurities and recover valuable components, maximizing economic benefits without increasing raw material usage.
- Purification and Solvent Recovery by distillation or melt crystallization. GEA’s advanced purification and solvent recovery technologies optimize liquid processes, achieving the highest purity while saving energy, water, and time. This not only reduces waste but also minimizes the need for virgin resources.
- Industrial Wastewater Treatment. In the face of growing water scarcity, GEA provides industrial wastewater treatment solutions, including zero-liquid discharge systems. Various GEA technologies help future-proof businesses by reducing water consumption and recovering valuable resources from wastewater streams.
- Waste Revalorization. GEA’s expertise in evaporation, crystallization, heat transfer, mixing, solid/liquid separation, distillation and drying allows manufacturers to redefine waste. Instead of discarding precious finite resources, companies can now recover valuable components from various waste streams, including end-of-life batteries, polycotton waste and PET plastic.
Pioneering Plastic Recycling Technologies
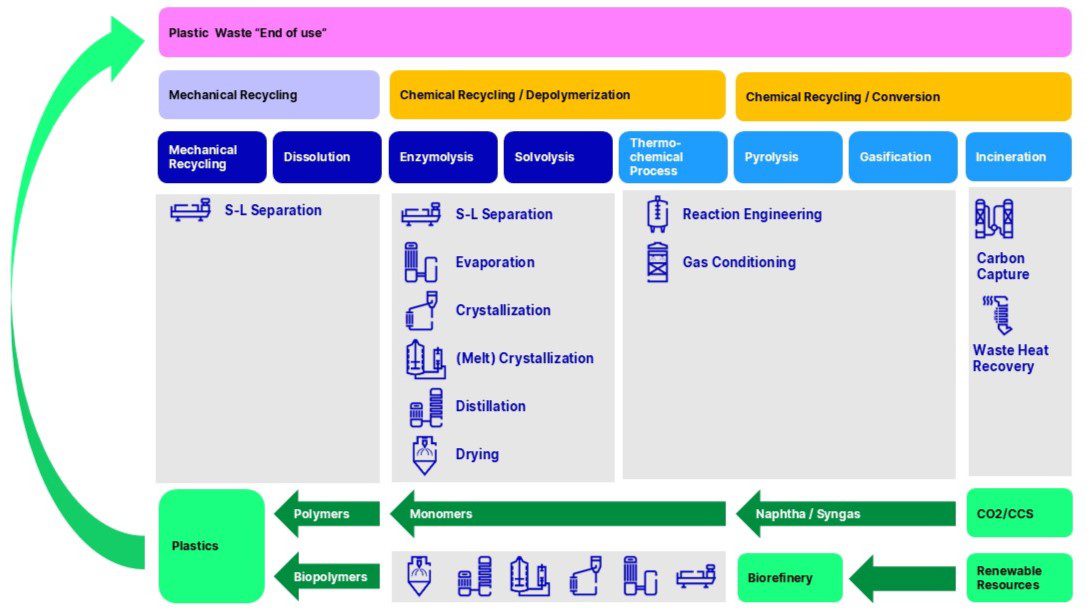
GEA’s wide range of technologies for plastic recycling.
Mechanical Recycling Processes: GEA provides substantial contributions, focusing particularly on separation techniques within mechanical recycling and solvent dissolution processes.
Depolymerization: GEA excels in processes like Enzymolysis and Solvolysis, leveraging its crystallization technologies to purify monomers. These monomers are essential for creating an extensive array of chemical intermediates or serving as a foundation for repolymerization.
Chemical Recycling: Processes such as pyrolysis, gasification, and other thermochemical methods benefit from GEA’s advanced gas conditioning and gas cleaning technologies.
Energy Recycling: When plastic recycling is limited to energy recovery, GEA’s Carbon Capture solutions play a crucial role. They capture emitted carbon, allowing for the reuse of both energy and carbon sources.
Numerous sectors of the chemical industry are already profiting from GEA’s comprehensive portfolio such as:
• Mechanical PET Recycling and Dissolution
GEA’s decanter centrifuges play a crucial role in the recycling of PET bottles. Additionally, GEA’s separation process technologies retrieve the in solvents dissolved polymers allowing a direct reuse.
• Depolymerization and Purification processes for PET Recycling
GEA’s crystallization process technologies make a significant environmental and economic contribution by transforming plastic waste into new reusable monomers, thereby reducing the carbon footprint. GEA provides essential technologies for extracting biopolymers, supporting the growing market for biodegradable and compostable plastics.
• Chemical Recycling in thermochemical processes
The elaborate process of chemical recycling is possible thanks to GEA’s technologies that depolymerize, separate, purify and refine complex molecular structures, ensuring the efficient and effective recycling of chemical compounds. In the conversion of plastic waste, gas conditioning is a key operational step, effectively performed by GEA’s gas cleaning technologies.
• Waste Electrical and Electronic equipment (WEEE)
Leveraging decades of experience in non-ferrous applications, GEA offers state-of-the-art dry gas cleaning plants designed to handle simpler waste streams. For more complex waste, GEA provides combined dry and wet systems that effectively reduce emissions and ensure the circularity of recycled metals from waste electrical and electronic equipment.
• Battery Materials Recycling
With over a century of expertise in evaporation and crystallization, GEA has designed centrifugal separators, evaporators and crystallizers suitable for all process steps of battery recycling. These technologies maintain the purity of recovered materials, making possible to use them to produce new batteries.
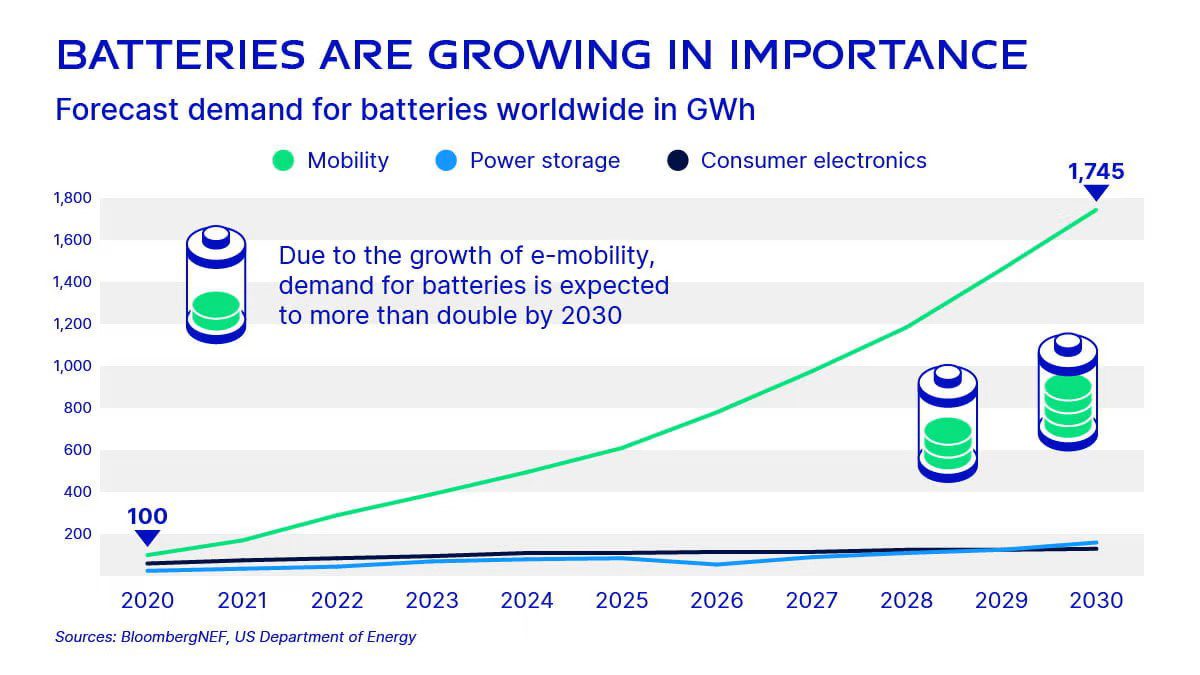
As battery demand grows, GEA’s capacity to recover valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, manganese and nickel with the highest purity turns more relevant.
• Carbon Capture solutions
GEA is accelerating the transition towards a low-carbon industry with advanced Carbon Capture Storage and Utilization (CCS/CCU) solutions that enable the efficient capture of CO2 from process-related emissions. GEA advanced Carbon Capture solutions prevent the release of CO2 into the atmosphere, utilizing or sequestrating it for either the production of valuable products or its long-term storage. This results in a significant contribution to industrial decarbonization and climate change mitigation.
As the chemical industry grapples with the challenges of sustainability, resource scarcity and disrupted supply chains, GEA is driving the circular transition towards more sustainable value chains. As we move towards a future where circularity is not just an aspiration but a necessity, GEA’s technologies and expertise will continue to play a crucial role in driving this transformative change across the chemical industry.